| AMPS
|
|
Advanced
mobile phone services |
| CTM
|
|
Cordless
terminal mobility |
| DECT
|
|
Digital
enhanced cordless telecommunications |
| ETSI
|
|
European
Telecommunications Standards Institute |
| GAP
|
|
General
access profile |
| GSM
|
|
Global
system for mobile communication |
| GSM
900 |
|
GSM in
the 900 MHz frequency range |
| GSM
1800 |
|
GSM in
the 1800 MHz frequency range |
| IN
|
|
Intelligent
network |
| Inmarsat
|
|
International
Maritime Satellite Organization |
| ITU
|
|
International
Telecommunication Union |
| LAN
|
|
Local area
network |
| LEOS
|
|
Low-earth-orbiting
satellites |
| MODACOM
|
|
Mobile
data communication |
| MOBITEX
|
|
Mobile
text transmission system |
| PBX
|
|
Private
branch exchange |
| PCS
|
|
Personal
communication services |
| PDA
|
|
Personal
digital assistant |
| PIC
|
|
Personal
intelligent communicator |
| PSTN
|
|
Public
switched telephon network |
| SMCS
|
|
Siemens
mobile communication service |
| TCP/IP
|
|
Transport
control protocol/Internet protocol |
| TDMA
|
|
Time division
multiple access |
| UMTS
|
|
Universal
mobile telecommunications system |
| VSAT
|
|
Very small
aperture terminals |
| WAN
|
|
Wide area
network |
| WLL
|
|
Wireless
local loop |
| X.25
LAN |
|
Packet-switched
LAN in accordance with ITU standard X.25 |
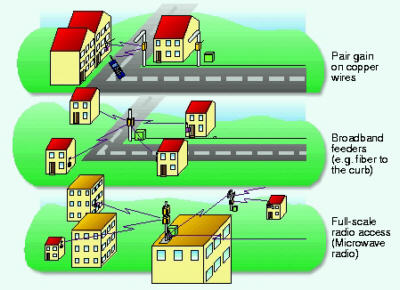
Examples of DECT networking within the
public network
WLL systems offer a wide
range of services for users with stationary terminal devices, as well
as local mobility for the users of mobile equipment. The application-specific
characteristics of the cellular networks and cordless networks are utilized
to an optimum extent where dual-band handsets and dual-mode
handsets are used, ensuring that a mobile subscriber can always be reached
at the most reasonable rate.
While a dual-band handset is used within two cellular networks,
a dual-mode handset can be used for applications within one cellular
network and one cordless network. Such criteria as the convergence of
fixed networks and mobile radio networks, extension of network capacity,
mobile radio for private users, EU directives and deregulation of the
telecommunication market are leading to the integration of DECT with
GSM in the form of dual-mode handsets.
Applications for Dual-Mode
Handsets
DECT and GSM are global standards, which apply to a wide product spectrum,
including cordless telephones, mobile telephones, GSM data modules for
data transmission and telemetry, as well as WLL products, GSM systems,
IN system components and IN services within GSM, PCS, wireless PBX and
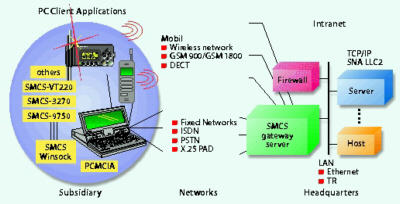
MODACOM servers.
Dual-mode handsets can be implemented and used within the DECT campus
sector (connected to the PBX) at home, connected to the public network
(PSTN, DECT sector), and on the road (GSM). Apart from voice communications
and applications via DECT and GSM, data communications are also offered
via mobile networks (DECT, GSM, MODACOM, MOBITEX) and fixed networks
(ISDN, X.25 LAN, PSTN).
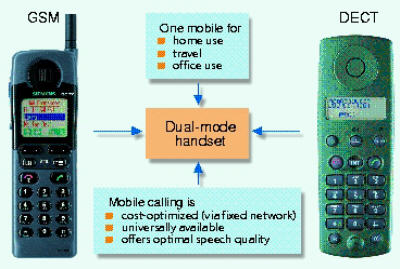
Dual-mode handsets integrate mobile
hand-helds with cordless telephone
User Benefits
Mobile products and solutions will ensure that the user can be reached
for voice, data and image communications at any location with DECT,
WLL and GSM. A specific user can be reached reliably and quickly, irrespective
of location, terminal device and network with one number service.
Applications based on GSM, DECT-GAP and DECT-WLL enable full-coverage
availability at home (DECT connected to the public network), in the
office (PBX with cordless telephone) and in the public sector (DECT-WLL).
Dual-mode terminal devices extend the local mobility of cordless DECT
through the global mobility of GSM. Global availability therefore grows
together with the service features of the PBX. As far as the user is
concerned, the most important benefits are location-independent availability
and the safeguarding of investments by using existing infrastructures
(PBX, LAN) and equipment.
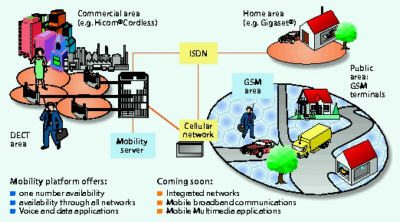
Application scenario for the marriage
of various telecommunication systems.
Toward the Universal Mobile
Network
The market for mobile communications is growing at an above-average
rate, as is the proportion of that market represented by data communications.
Interesting mobility applications for voice, data and image are available
today, based on existing networks. These are being expanded continuously
and adapted to future standards.
Interworking between DECT, GSM and fixed networks plays an important
role with respect to optimum utilization of the service features offered
by various networks. The resources and mobility functions of different
networks are at the user's disposal as a result of this. GSM and DECT
will merge to produce the UMTS over the long run. Apart from the integration
of DECT and GSM, the multi-band and multi-mode handset will
play a significant role along this road. The significance of mobile
data communications is increasing continuously with regard to applications
(teleworking, mobile office, telemetry), multimedia terminal devices
(PIC/PDA, remote Internet access), and networks.